Rhythm Recognition
Knowing how to read and interpret ECGs is a critically important skill in ACLS and PALS. Take a moment to review the most common cardiac rhythms encountered in ACLS and PALS.
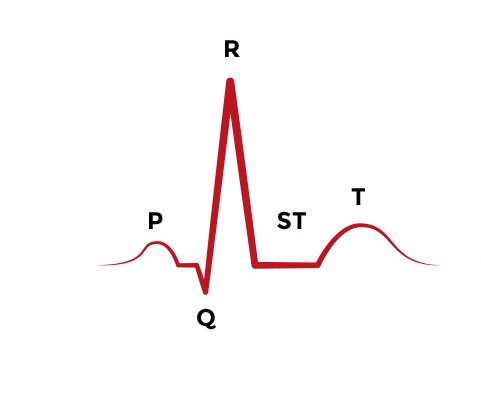
The Prototypical ECG Tracing
The P wave corresponds to electrical impulse traveling through the atria. This is synonymous with atrial depolarization and usually corresponds with atrial contraction.
The QRS complex corresponds to the depolarization of the left and right ventricles. It generally corresponds to the contraction of the ventricles.
The T wave corresponds to a repolarization of the ventricles.

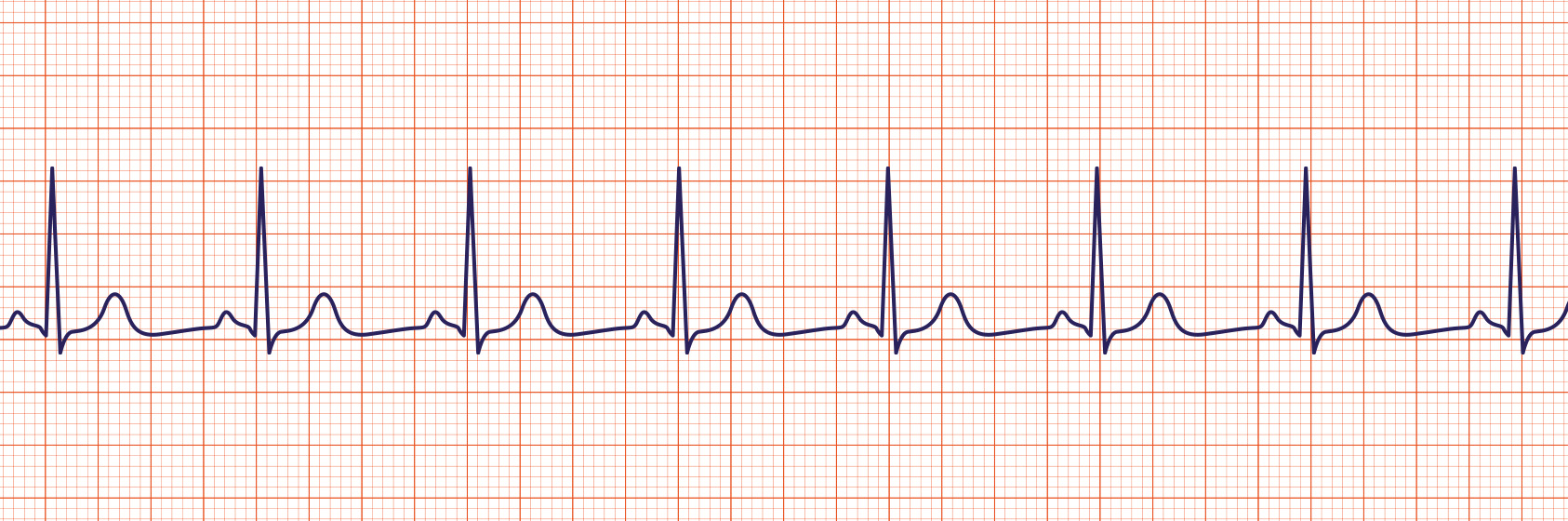
Sinus Rhythm
A sinus rhythm is regular with normal P, Q-R-S, T deflections and intervals. Rate = 60-100 at rest.

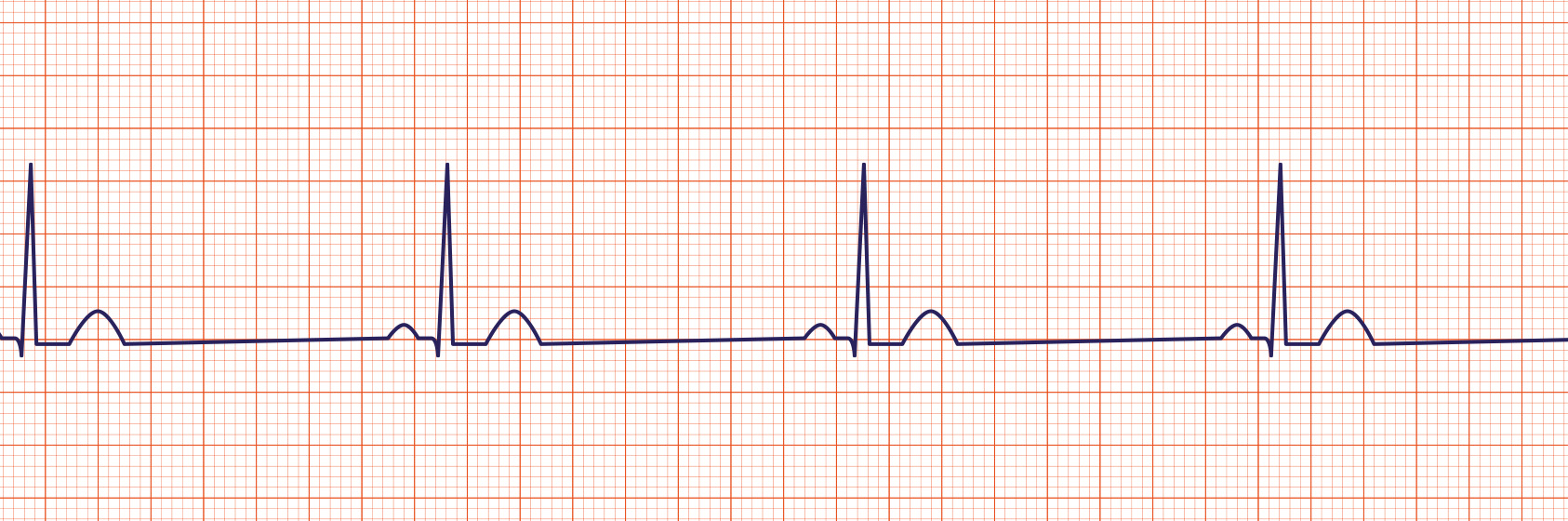
Sinus Bradycardia
Sinus bradycardia is a sinus rhythm with a rate less than 60 per minute in an adult.

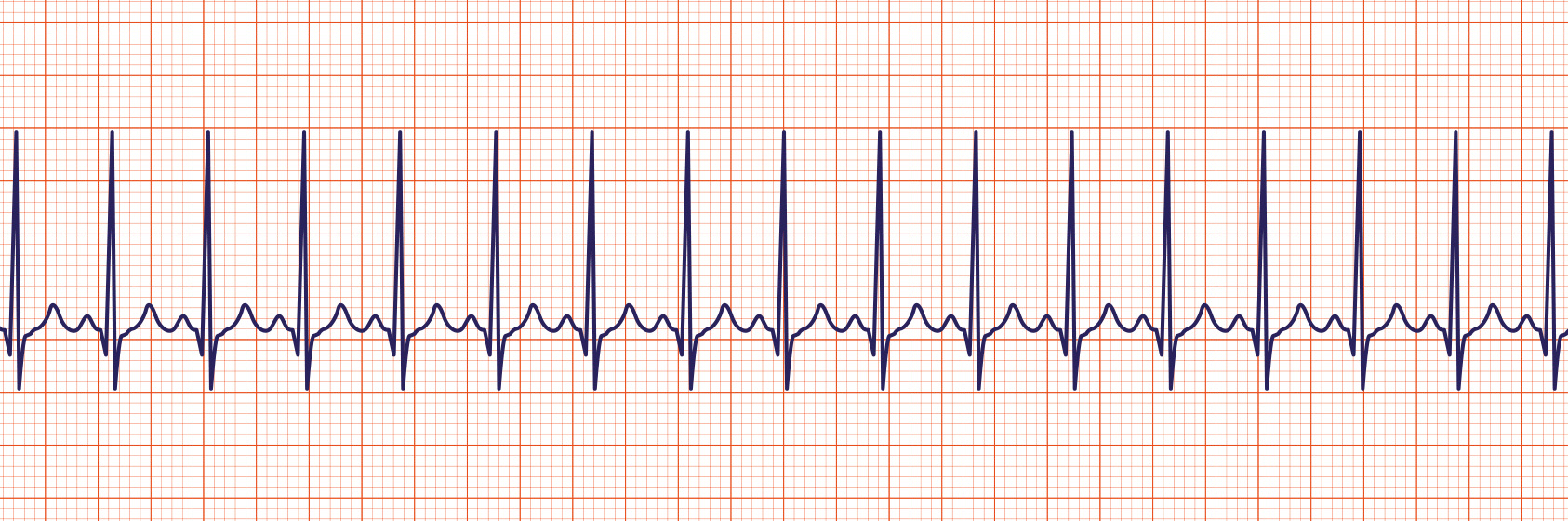
Sinus Tachycardia
Sinus tachycardia is a sinus rhythm with a rate greater than 100 per minute in an adult. Note that the p waves are still present.

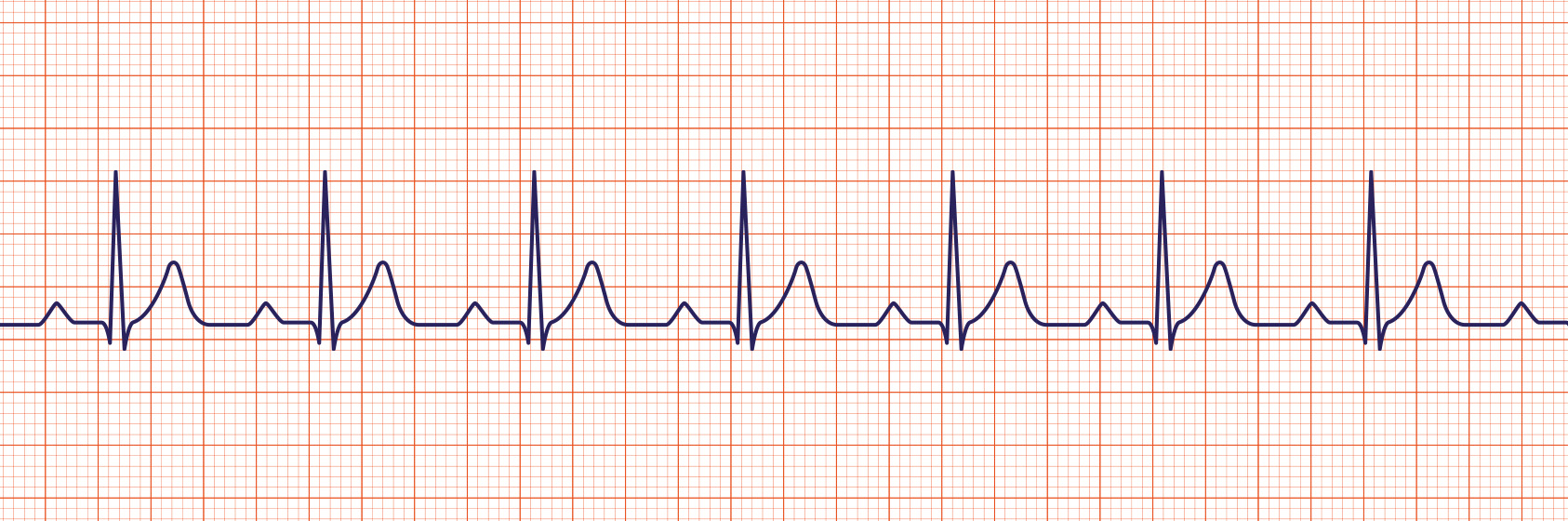
First-Degree Heart Block
Sinus rhythm with 1st degree heart block is a sinus rhythm with a prolonged PR interval > 0.20 seconds due to a delay in transmission from the atria to the ventricles.

Second-Degree AV Heart Block
A 2nd degree AV block is usually classified as Mobitz Type I (Wenckebach) or Mobitz Type II. A Mobitz Type I heart block is characterized by progressive lengthening of the PR interval until a QRS complex is dropped.
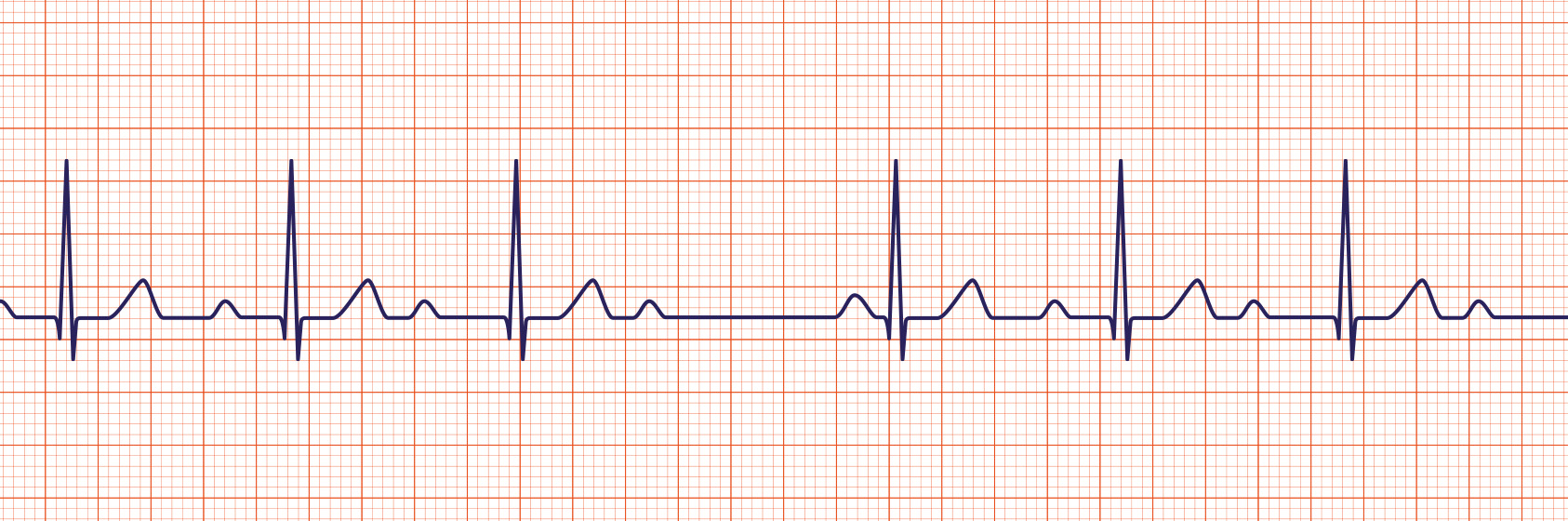

A Mobitz Type II heart block is characterized by an intermittent dropped QRS that is not in a Mobitz Type I pattern. The Mobitz Type II block must be evaluated since it is one that can rapidly progress to a complete heart block.
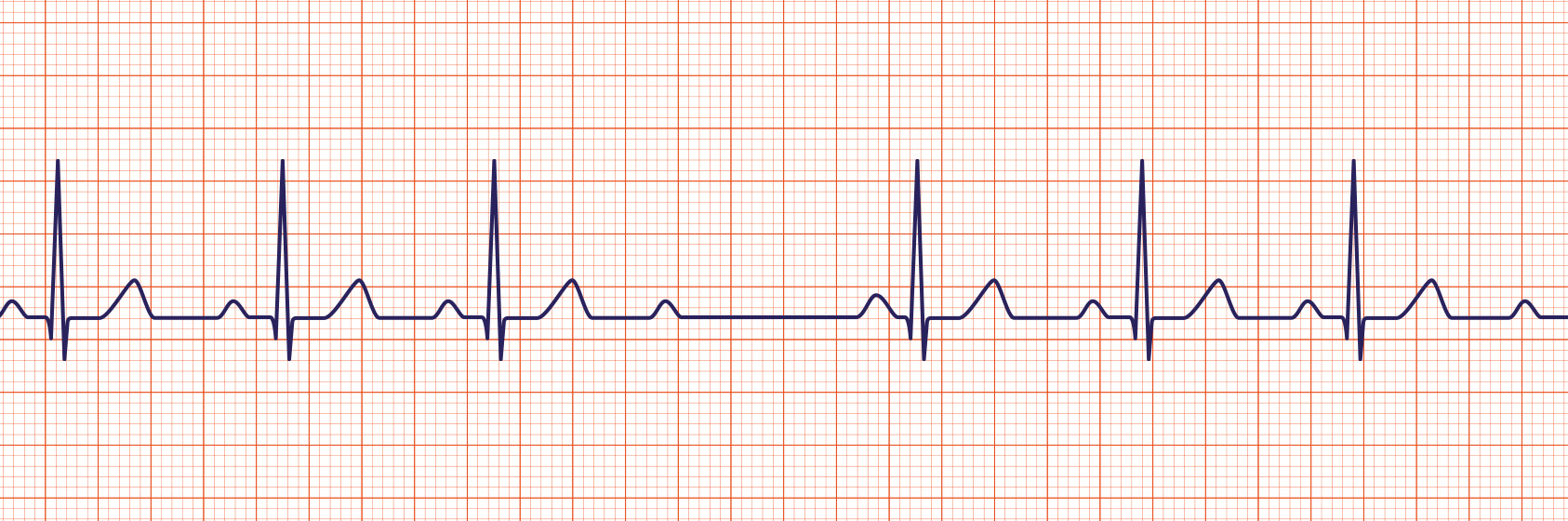

Third-Degree Heart Block
A 3rd degree heart block (sometimes called a complete heart block) is a rhythm in which there is no relationship between the P and QRS waves. In this case, the P to P intervals are regular but have no relationship to the QRS complexes on the ECG.
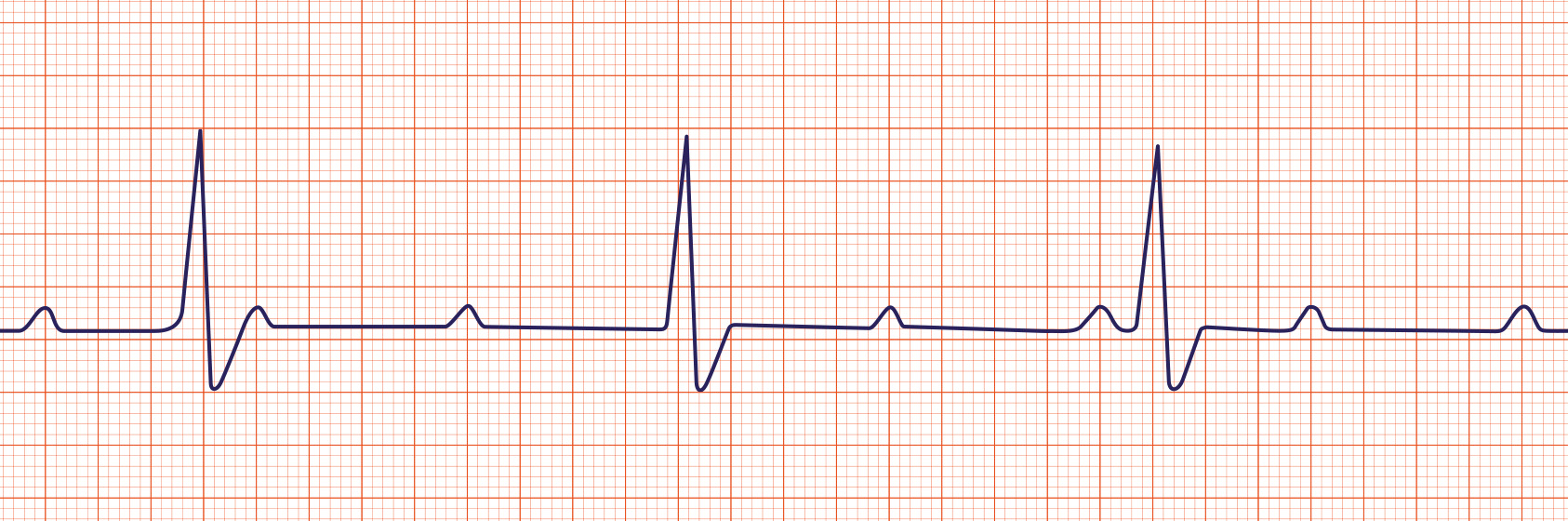

Supraventricular Tachycardia
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is an extremely fast atrial rhythm with narrow QRS complexes when the impulse originates above the bundle branches (above the ventricles).
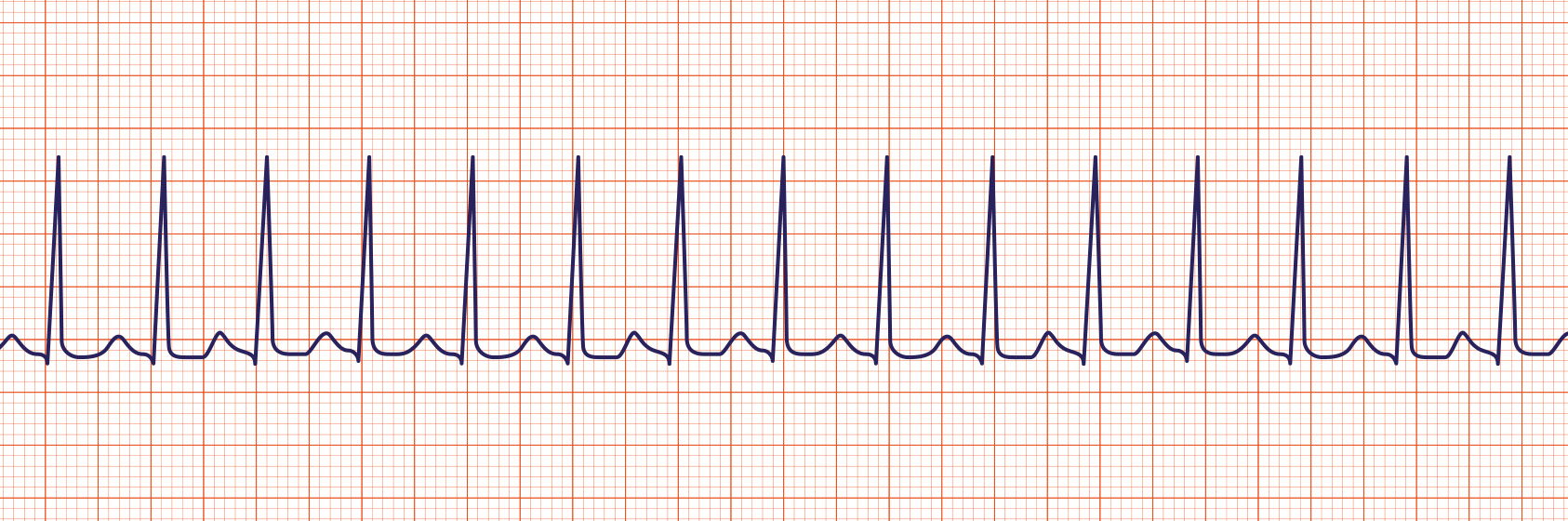

Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial Fibrillation (Afib or AF) is a very common arrhythmia. This rhythm is characterized by no waves before the QRS complex and a very irregular heart rate.
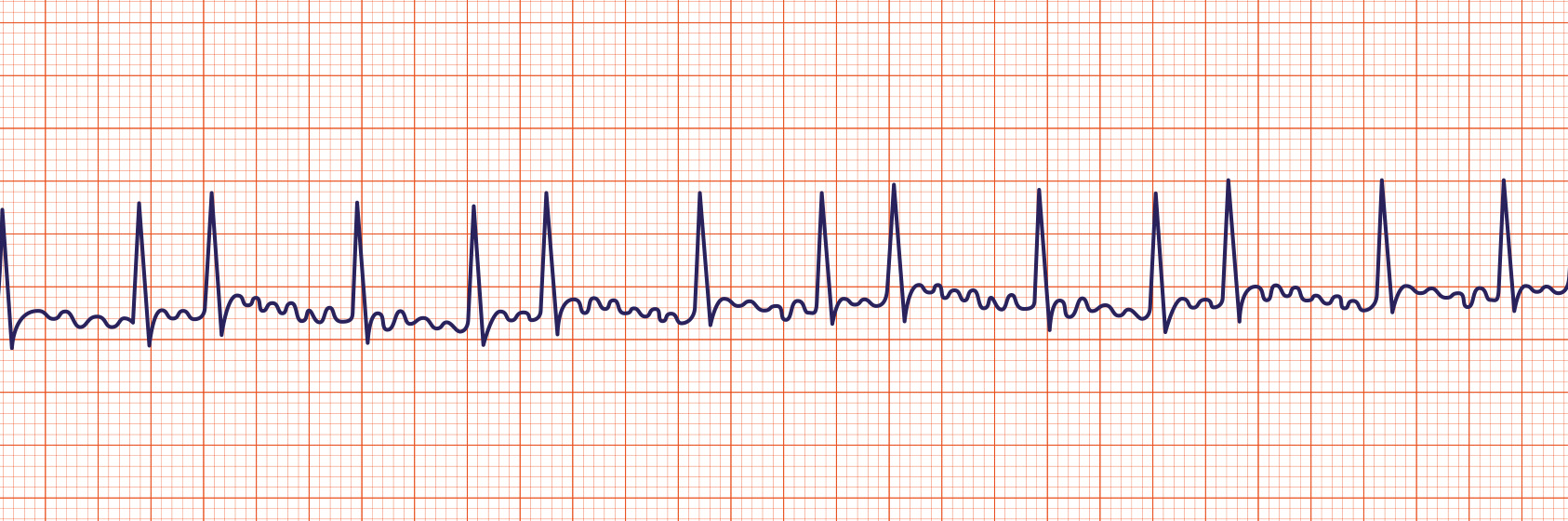

Atrial Flutter
Atrial flutter is a supraventricular arrhythmia that is characterized by a “saw-toothed” flutter appearance on the ECG that represents multiple P waves for each QRS complex.
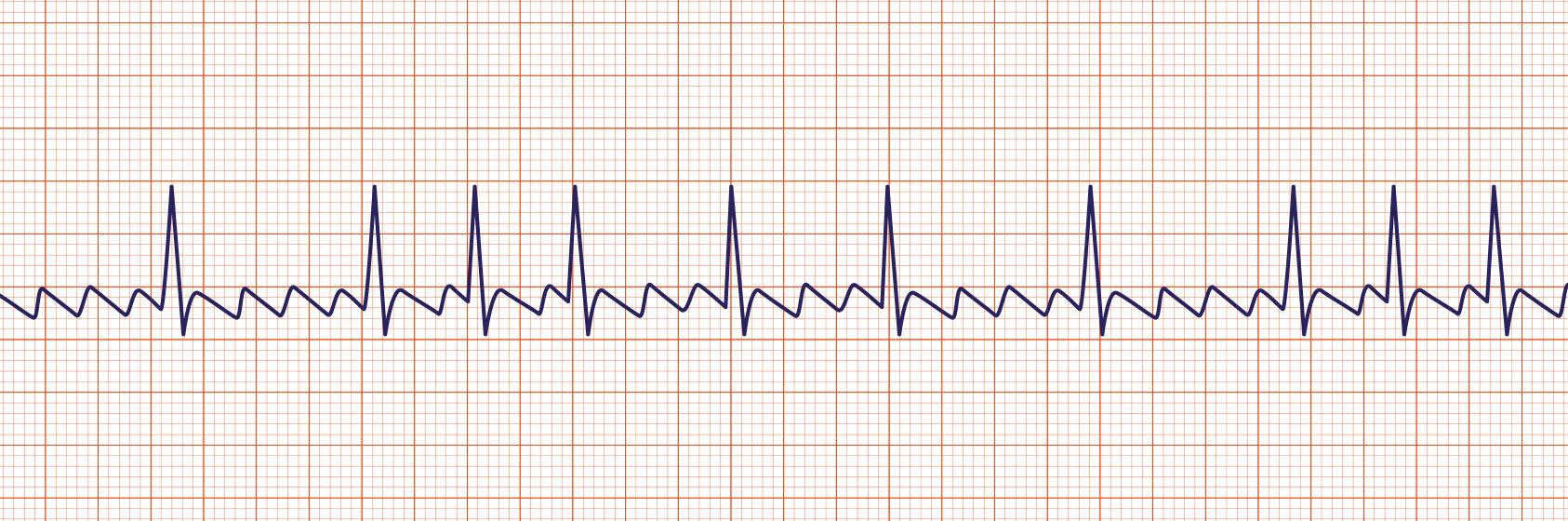

Asystole
Asystole is also commonly known as a “flat line” where there is no electrical activity seen on the cardiac monitor. Not responsive to electrical defibrillation.
Pulseless Electrical Activity
Can be virtually any organized ECG rhythm in a patient who is unresponsive and lacks a palpable pulse. Thus, one cannot learn a PEA rhythm. It should not be confused, however, with specific pulseless scenarios listed previously.
Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia (Vtach or VT) is characterized by bizarre widened QRS complexes, no P waves and usually a rate over 100 per minute. May quickly degenerate to Ventricular fibrillation and death. VT may be responsive to electrical defibrillation.
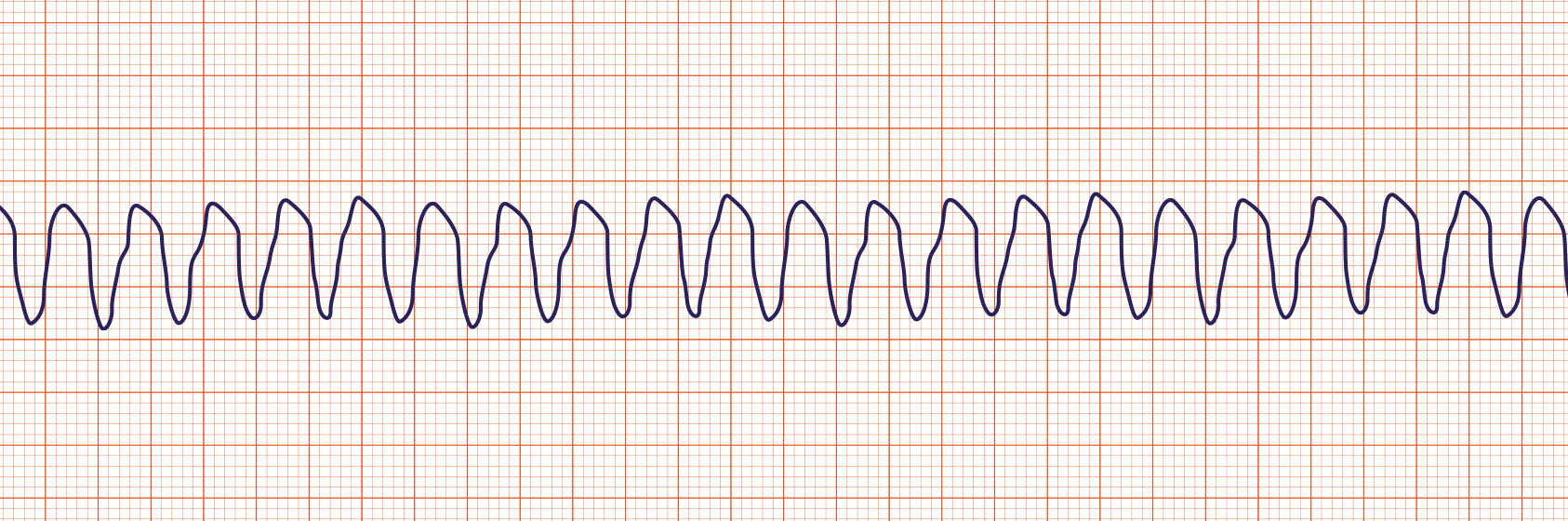

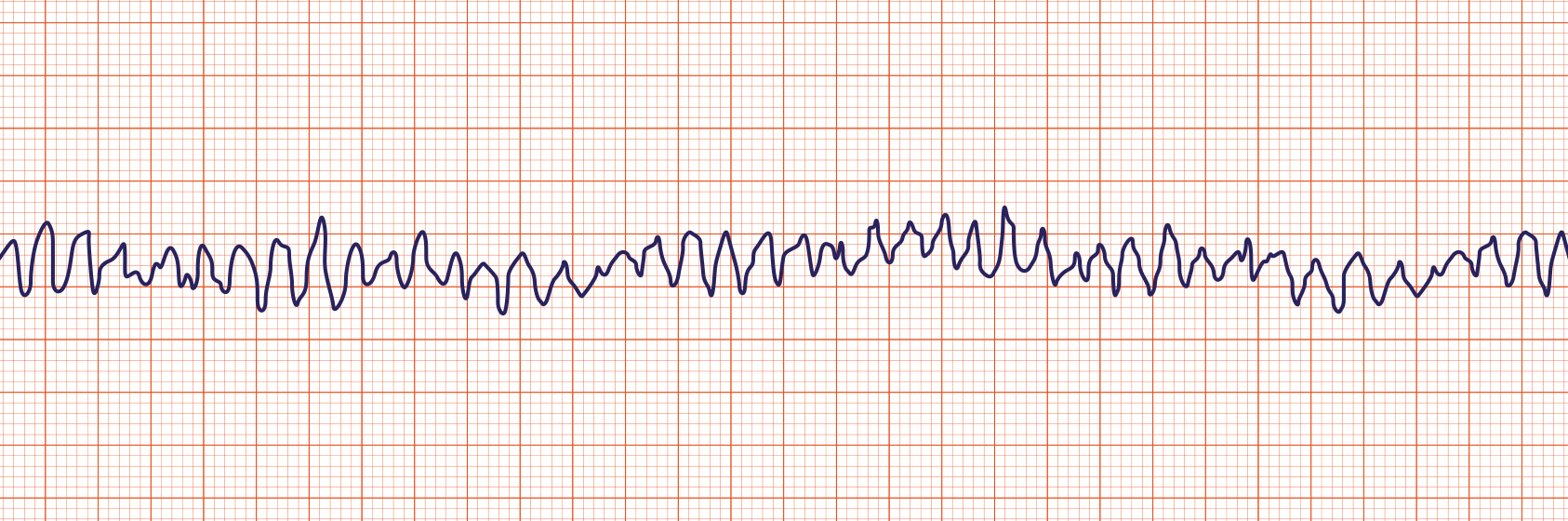
Ventricular Fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation (Vfib or VF) is characterized by a chaotic wave pattern and no pulse. VF may be responsive to electrical defibrillation.